

Cybersecurity is the biggest concern for every industry today. With everything present digitally and virtually, it has become a highly crucial factor for data present online. Plus, companies are now entirely dependent on email communications for every official purpose. Therefore, security against the constantly email-based cybercrimes like phishing attacks has also become a huge fear factor for every organization.
Table of Content
What is Phishing Attack and How does it Work?
Phishing attack is basically the most common but dangerous cyber-attack vector that is capable of exploiting the entire data of an organization with one click! It is a fraudulent attempt to gain user’s sensitive information and financial information for the vicious intent. This attack is deployed via email or by creating any illegitimate web page or site of an official entity to dupe users.
It is the most successful social engineering technique that is used for deceiving users into handing over their confidential data. Cyber threat actors usually target users by the medium of communication as they pretend to be from legitimate sources. These sources can be websites, banks, IT administrators, government agencies or auction houses, etc.
In technical terms, it is an online theft where cyber frauds trick users to steal and exploit their data present online. This cyber theft practice is attempted through email, instant messaging, voice calls, fax, etc. These attacks are divided into two categories:
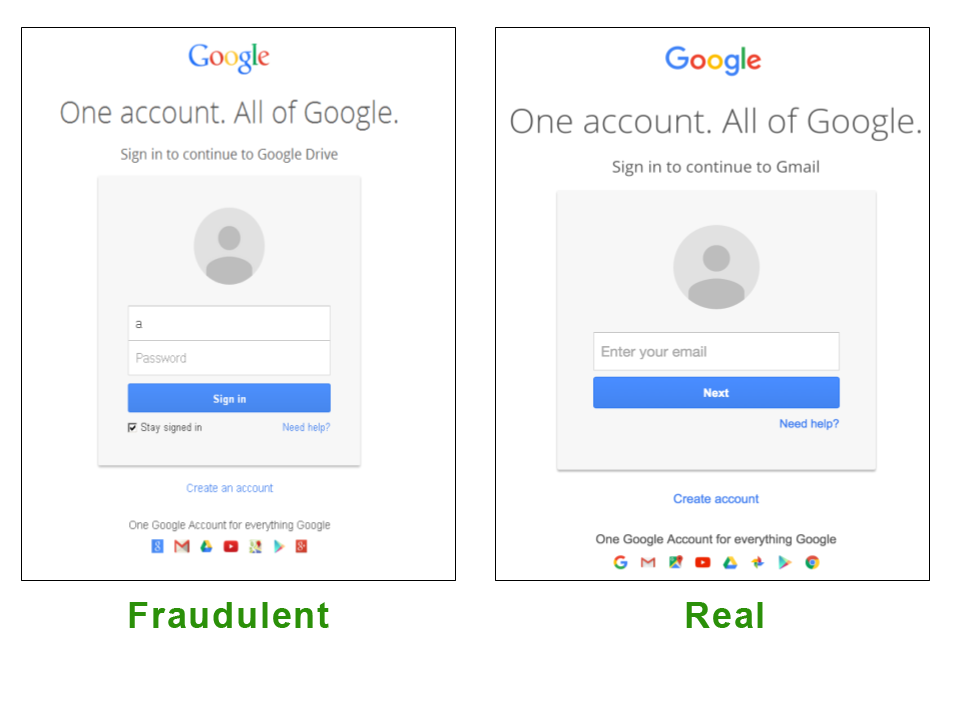
- Spoofed websites:
A platform to trick users into providing sensitive details on the data harvesting sites by compelling them through email or SMS communication.
- Malware installation:
Fraudsters lure users to install malware by clicking on a download link that seems to have come from a legitimate source.
Currently, businesses are the most affected targets of phishing attacks. Reportedly, today phishing attacks have accounted for more than 80% of security incidents and a loss of $17,700. Whereas, according to the survey, around 94% of emails consist of malware and malicious attachments. 56% of the IT decision-makers believe that phishing attacks are the biggest cybersecurity threat to organizations as almost 32% of data breaches involve phishing.
How to Protect Against a Phishing Attack?
Phishers become empowered during any public crisis, regardless of the severity of the situation. They become opportunistic and search for advanced ways to deploy cyber attacks. In fact, they have squeezed out of every opportunity to such an extent that today these cyber threat actors are misusing the COVID-19 pandemic for fraudulent practices.
In this fast-growing influx of COVID-19 phishing attacks, cybercriminals are deploying email scams and are creating fraud website domains to misguide people, especially employees working from home. According to security research, over 16,000 new domains related to Coronavirus were registered from the beginning of January 2020 and the number has been multiplying rapidly ever since!
Moreover, among these Coronavirus-related website domains, most of the pages or sites were found to be malware loaded. No wonder how these phishing attacks are getting more sophisticated day by day and very unprecedented in nature. But, if taken proper preventive measures and implemented better phishing attack solutions, one can avoid falling victim to it.
Here are the following ways to protect against phishing attack:
1. Check for SSL certificate
Always check and verify the site that asks for your personal or even general information. Some URLs might begin with http:// and others with https://. The only difference is having ‘s’ on the web address. In order to verify the authenticity of a website, always check for https:// and the closed lock icon on the web address.
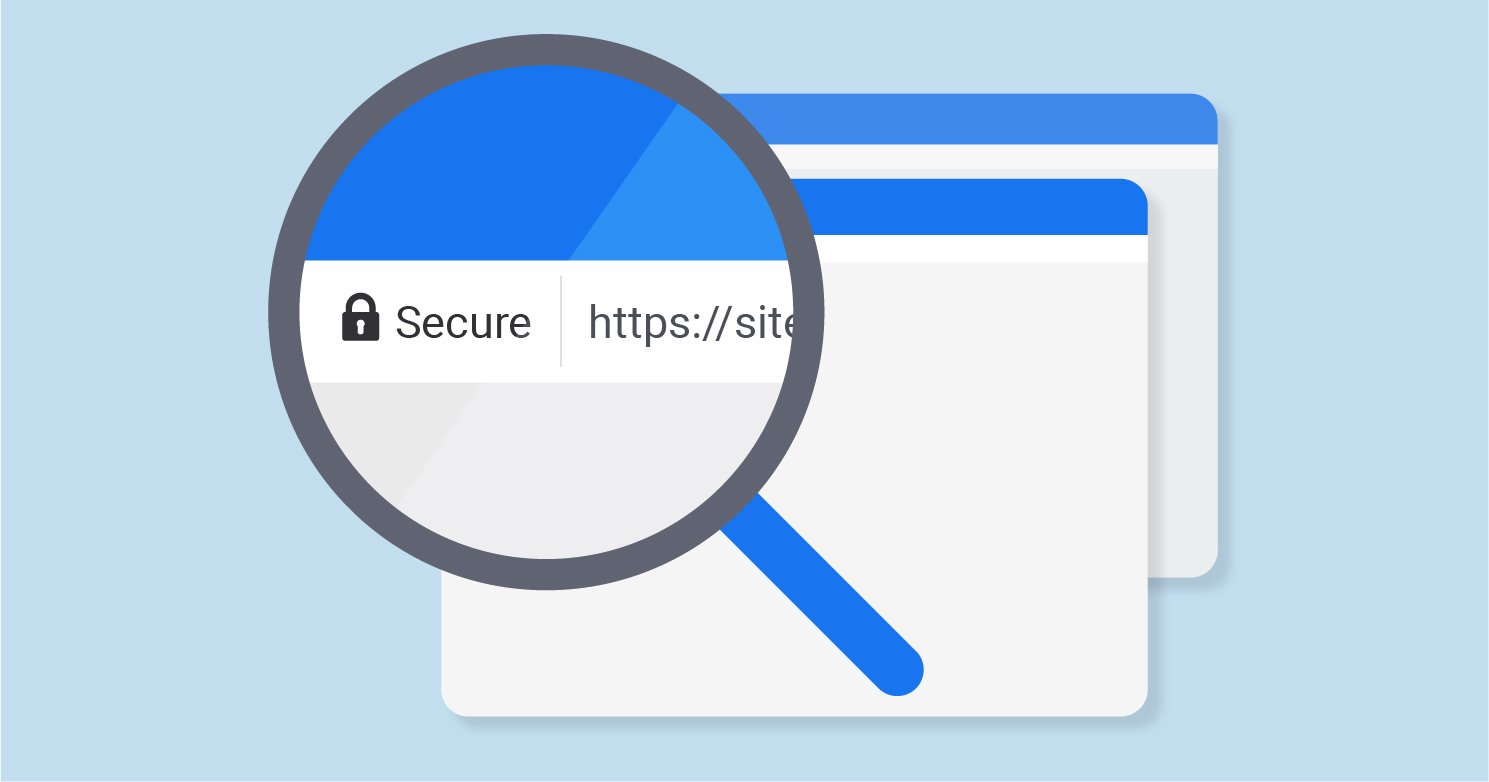
The ‘s’ basically stands for secure which means the website is safe to use. Also, if you click on an email link that redirects you to a website then make sure to verify the site’s SSL credentials first. The SSL certificate ensures secure and encrypted data transmission over the internet.
2. Lookout for grammatical errors
When it comes to creating a look-alike website or email, phishers can be good with coding but are often bad at writing content. Professional copywriters always ensure the quality of the content and make certain to send well-tested content with almost no error or flaw. One can detect a phishing email or website by checking the quality of the content. For example, poor grammar, illogical content flow, etc. is most likely done by inexperienced cyber scammers or frauds.
3. Phishing attack simulation training
As cybercrimes are on the rise today, organizations are expected to buckle up and train their employees for unpredicted future security threats. The best way is to educate employees about the importance of cybersecurity in an organization and what preventive measures they should take to mitigate cyber risks. Also, seeing how employees are the most vulnerable resource in any organization, it is important to train them with the help of phishing attack simulation. There are tools that offer the training of phishing attack simulation for employees in order to make them proactive in identifying phishing websites and emails.
4. Pop-ups are not always friendly
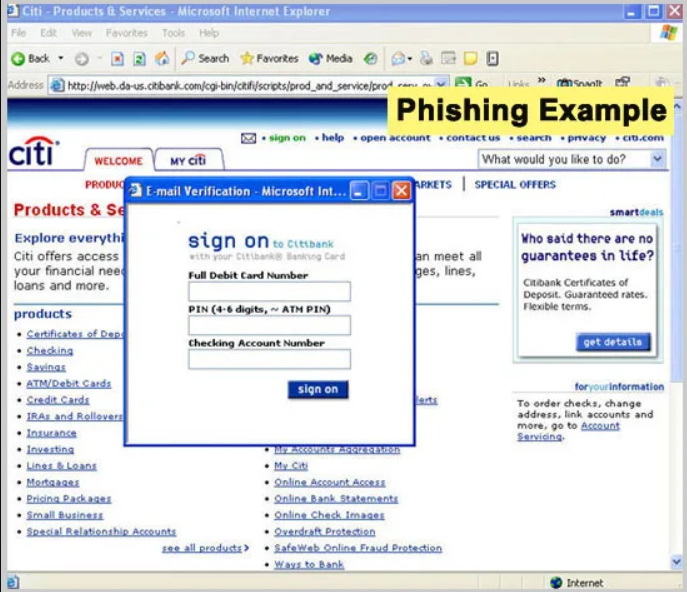
Avoid entering your personal information in pop-ups that appear on insecure websites. These pop-ups use Iframe technology to capture the user’s information and send it to a different domain. Although renowned and reputed websites will never ask for personal information on pop-ups, forged domains and spoofed sites can easily trick users into handing over their sensitive information.
5. Phishing incident response tool
Not every email landing in your inbox is a legitimate email because according to a survey, there is always 1 email out of 99 emails which is a phishing attack. Similarly, every 1 in 25 branded emails is a phishing email. Therefore, it is important to verify emails to check their authenticity and to do so, there are various advanced email security solutions available today. In case you find an email suspicious and fraudulent in nature, make sure to report it to a phishing incident response tool for the verification. Such tools provide real-time service to report, verify and resolve email-related issues.
6. Stay cautious of shortened links
The best way to trick any user into clicking on malicious or fake links is by sending shortened links that do not expose the real name of a website. Hackers use these shortened links to redirect users to fraud websites and obtain their personal information easily. To avoid becoming a target of such scams, always place the cursor on the provided short link to check the redirecting location before clicking on it.
7. Update all security patches
Keeping all the security patches up-to-date will not only mitigate the chances of cyber attacks but will also offer a cyber-resilient working environment. Hackers and cybercriminals majorly look for vulnerabilities in systems, software or applications to gain unauthorized access and exploit user’s data. For the best practice, always keep your system and web browsers up to date with the latest versions. The main purpose of this is that all these recent updates are released in response to security loopholes that hackers and cyber attackers seek for.
8. Avoid unexpected alarming emails
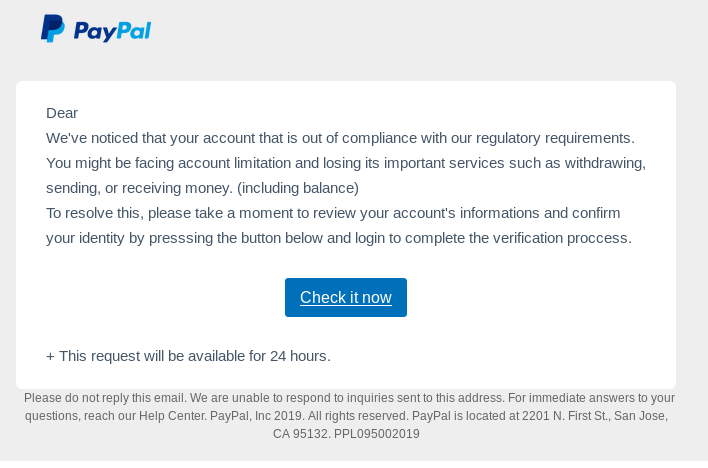
One of the best techniques phishers use is sending panic-creating emails that contain alarming content. These emails are popular with subject lines such as Alert, Deadline, Urgent Request, etc., to provoke users to respond.
It is always better to avoid such emails and specifically the unexpected ones that ask for urgent data submission or requests for downloads. You must always get such emails verified by the IT security administrator of your organization before taking any action to revert.
9. Double-check the sender’s email address
The first step to identify whether an email is legitimate or not is to always check the email address of the sender. Cyber thieves create spoofed email addresses to dupe users into thinking that the email has come from a legitimate source. Moreover, without giving a second glance, victims directly reach for email attachments. It is important to understand how the mindset of phishers works and how vulnerable we are left due to our negligence.
10. Anti-phishing, fraud monitoring & takedown tool
An organization’s reputation is very important on a digital platform as today most of the business comes from online resources and researches. Your brand represents your reputation online so it is essential to monitor activities taking place online in the name of your firm. Cyber fraudsters have now become more advanced and are using more complex methods to trick users for their malicious intent. Phishing websites are one of the widely used methods to dupe and diverge customers from the legitimate website of an organization to a look-alike fraud page. Security admins must implement an anti-phishing, fraud monitoring & takedown tool to monitor phishing and fraud activities taking place in the name of the organization. Once tracked, these fake domains can be instantly taken down the web browser to stop copyright infringement online.
Do You Know
Who Is The Weakest Link In The
Cyber Security Chain?
You will be shocked but…it is your EMPLOYEES!
Make your employees proactive against prevailing cyber attacks with ThreatCop!

